Como a inteligência humana saiu das cavernas e chegou à era da IA
Há muitos milênios, os primeiros seres humanos começaram a fabricar ferramentas simples de pedra. Mais tarde, há cerca de um milhão de anos, dominaram o poder do fogo. Essa descoberta foi transformadora — as chamas forneceram calor, possibilitaram o cozimento dos alimentos, ofereceram proteção e reuniram comunidades. Ao longo das sucessivas eras da pedra, do bronze e do ferro, com o desenvolvimento da agricultura, dos centros urbanos e da linguagem escrita, a civilização foi tomando forma, estabelecendo sociedades organizadas, crenças espirituais, expressão artística, sistemas legais e redes de comércio.
Posteriormente, surgiu o Renascimento, seguido pela Revolução Científica e pela industrialização, inaugurando um período de progresso extraordinário. A energia a vapor, os avanços científicos, as descobertas médicas e as inovações nos transportes revolucionaram a existência humana. As pessoas passaram a questionar tradições estabelecidas, abrindo caminho para a era elétrica do século XX, a revolução da computação, a expansão das telecomunicações e a conectividade da internet. Hoje, testemunhamos mais um salto monumental com a inteligência artificial — máquinas que aprendem, auxiliam o pensamento, estimulam a criatividade e viabilizam a colaboração.
Estamos em um momento decisivo: a humanidade carrega toda essa herança, do domínio do fogo à inteligência artificial. Cada época trouxe novos desafios e aspirações de progresso. A revolução da inteligência artificial representa mais um marco crucial: ela pode ampliar nossas capacidades, mas precisamos garantir que esse poder não gere problemas ou desigualdades, tornando-se, em vez disso, uma oportunidade de avanço coletivo.
Era Paleolítica: o começo de tudo

Se você pudesse visitar qualquer um desses períodos históricos, qual escolheria e por quê?
Desde os tempos antigos, quando os seres humanos caçavam e coletavam seu sustento, a descoberta do fogo tornou-se um dos marcos mais decisivos do desenvolvimento humano. As chamas trouxeram calor em ambientes frios, ajudaram a afastar criaturas perigosas e permitiram que nossos ancestrais cozinhassem os alimentos, tornando-os mais seguros e nutritivos — o que inclusive contribuiu para o desenvolvimento do cérebro.
Além disso, o fogo fortaleceu a conexão humana: as noites ao redor das fogueiras tornaram-se momentos de conversa, contação de histórias, criação de mitos, troca de conhecimentos e construção de laços. Ele também possibilitou a ocupação de regiões mais frias, forneceu iluminação noturna e permitiu a fabricação de ferramentas com uso do calor, demonstrando que o fogo não foi apenas uma descoberta, mas um impulsionador da cultura, da tecnologia e da formação das comunidades.
Período Neolítico: o catalisador da agricultura e da vida em comunidade

O que impulsionou o início do desenvolvimento social humano?
Durante o período Neolítico, a humanidade passou por uma transformação profunda ao adotar a agricultura e a domesticação de animais. Essa mudança decisiva permitiu que as pessoas abandonassem o nomadismo e estabelecessem comunidades fixas em aldeias permanentes. Com o surgimento da agricultura, formaram-se os primeiros grupos sociais organizados, possibilitando o trabalho cooperativo, a troca de bens e o início do desenvolvimento urbano.
Esse novo modo de vida introduziu uma economia cooperativa, na qual a interdependência entre os membros da comunidade tornou-se essencial para a prosperidade coletiva.
Tempos Antigos e as Grandes Civilizações

Se você pudesse visitar essa era, qual aspecto mais despertaria seu interesse para explorar?
As grandes civilizações da Mesopotâmia realizaram feitos fundamentais que ajudaram a moldar o mundo como o conhecemos hoje: inventaram a escrita cuneiforme para registrar comércio, leis e histórias; criaram o Código de Hamurábi, um dos primeiros sistemas jurídicos da humanidade; desenvolveram a roda, sistemas de irrigação para a agricultura e alcançaram avanços significativos em matemática e astronomia.
No Egito Antigo, construiu-se uma sociedade altamente organizada ao longo do rio Nilo. Os egípcios criaram a escrita hieroglífica, ergueram monumentos impressionantes como pirâmides e templos, avançaram em engenharia, arquitetura e medicina, além de manterem um governo central forte que garantia estabilidade e rituais religiosos sofisticados.
Mais tarde, na Grécia e em Roma, o pensamento filosófico floresceu com a política — especialmente a democracia grega e o direito romano —, a arte e o teatro. Foram construídas estruturas grandiosas como teatros, templos e aquedutos. A filosofia grega introduziu novas formas de pensar, refletir e agir eticamente, ainda relevantes hoje, enquanto Roma organizou sistemas legais, expandiu impérios e difundiu cultura, língua e arquitetura por vastas regiões.
Idade Média: Luz Sob a Sombra
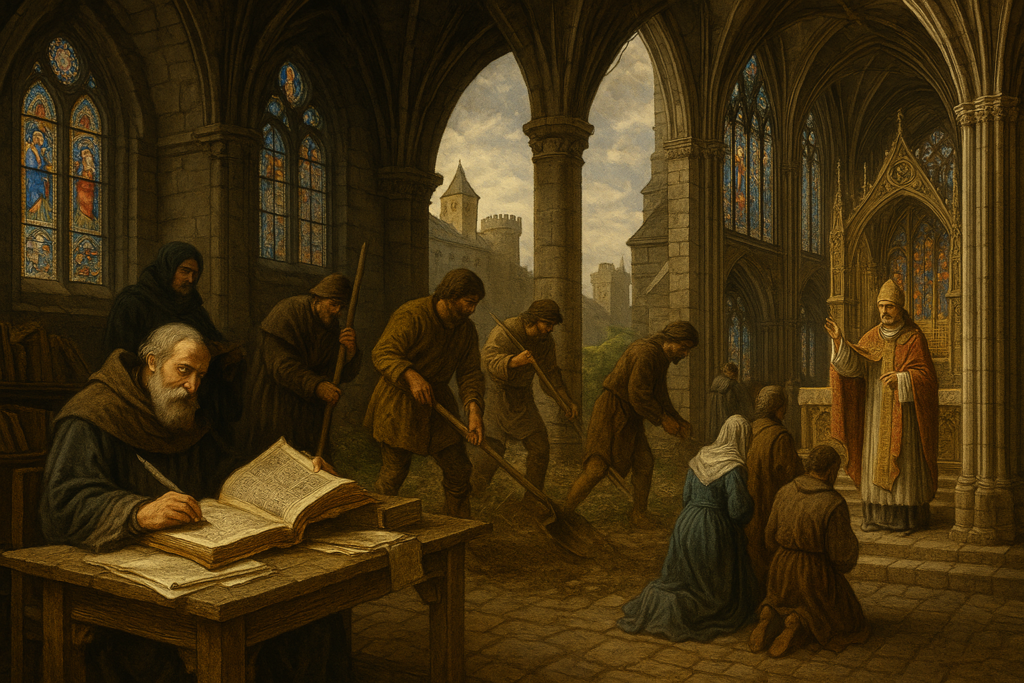

Como um período chamado de “Idade das Trevas” pôde, na verdade, iluminar conhecimentos que guiariam o futuro da humanidade?
Apesar de conflitos, crises e limitações, a Idade Média foi um tempo de intensa construção intelectual e social. Foi nesse período que surgiram algumas das mais importantes instituições educacionais da história. Universidades como Bolonha, Paris e Oxford nasceram a partir de escolas eclesiásticas, ensinando disciplinas como gramática, lógica, matemática, astronomia e teologia. Esse ambiente despertou entusiasmo entre mestres e estudantes, incentivando a tradução de textos antigos e o estudo sistemático da natureza.
Ao mesmo tempo, importantes inovações agrícolas transformaram a vida cotidiana. O arado pesado, a coleira de cavalo e o sistema de rotação de culturas em três campos permitiram o cultivo de solos mais difíceis, aumentaram a produção de alimentos e sustentaram o crescimento populacional.
A arquitetura também expressou esse florescimento. Castelos imponentes e catedrais góticas não simbolizavam apenas poder e fé, mas também conhecimento técnico e sensibilidade artística. Vitrais, abóbadas elevadas e esculturas transformaram esses espaços em centros de convivência, espiritualidade e expressão cultural.
Longe de ser apenas um tempo de estagnação, a Idade Média preparou o terreno intelectual, tecnológico e social que tornaria possível o despertar do pensamento crítico e das descobertas que viriam a seguir.
Renascimento: Questionamentos e Novas Descobertas
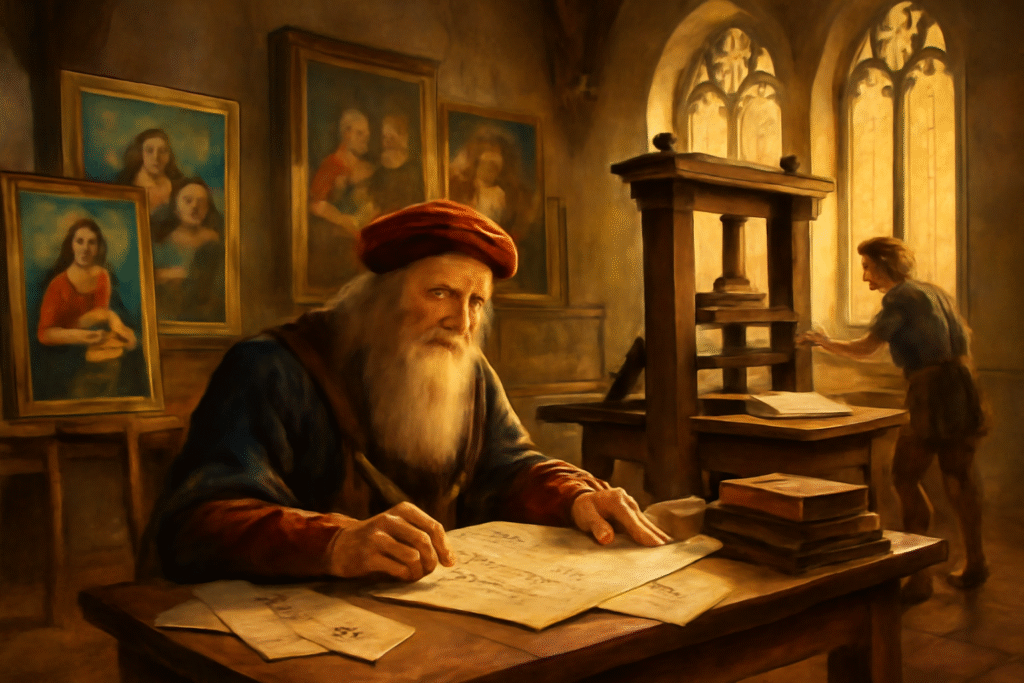

Se eu pudesse explorar esse período transformador, escolheria três frentes centrais da Renascença, porque nelas nasce o mundo moderno como o conhecemos:
1) O encontro entre arte e ciência
Ver de perto como Leonardo da Vinci estudava anatomia, engenharia e pintura ao mesmo tempo seria fascinante. A Renascença quebra a separação entre “exatas” e “humanas”. O conhecimento era integrado. Entender como eles observavam o corpo, a natureza e o movimento ajudaria a recuperar algo que perdemos hoje: a curiosidade total, sem rótulos.
2) O nascimento do indivíduo consciente
Esse período marca a virada em que o ser humano passa a se perceber como autor da própria história. Retratos, autobiografias, cartas e obras revelam emoções reais. Eu exploraria como essa nova visão de “eu” mudou ética, política, educação e até a noção de responsabilidade pessoal. É aí que começa a ideia de liberdade intelectual.
3) A revolução silenciosa da educação e da imprensa
A imprensa de Gutenberg multiplicou ideias como a internet faria séculos depois. Eu gostaria de acompanhar como livros começaram a circular fora do controle exclusivo da Igreja, acelerando debates, ciência e pensamento crítico. Foi o início da democratização do saber — com todos os conflitos que isso trouxe.
Em resumo:
A Renascença não foi só um período bonito — foi um ensaio geral da modernidade. Ela nos ensina que progresso verdadeiro acontece quando imaginação, método e coragem de questionar caminham juntos.
E talvez a pergunta mais atual seja:
👉 Estamos vivendo hoje uma nova Renascença — desta vez digital — ou apenas repetindo seus erros em escala maior?
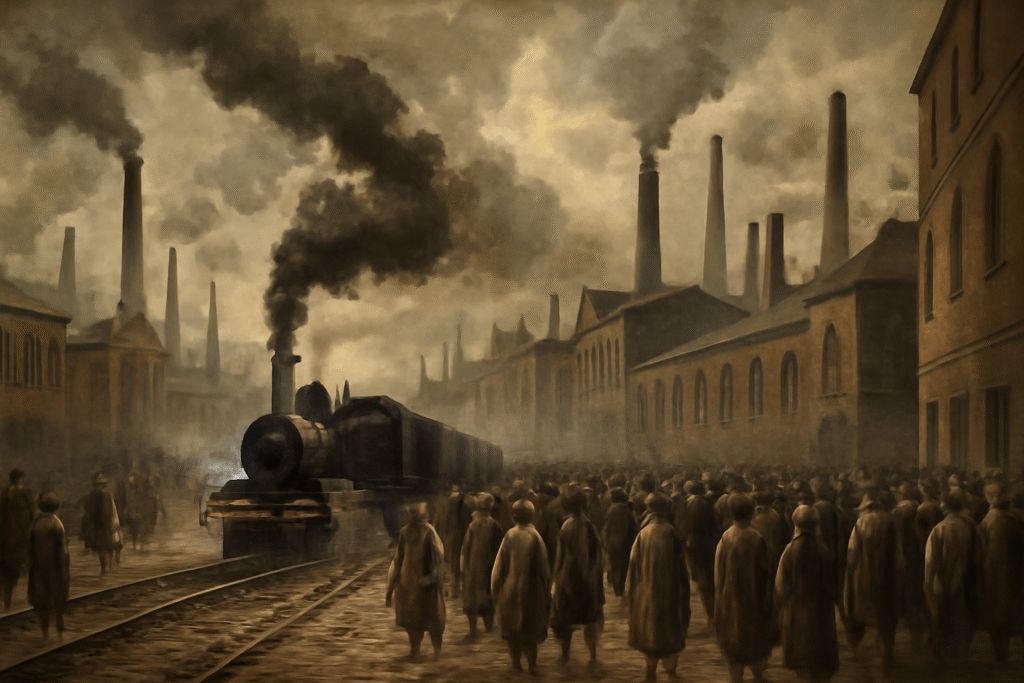

Se eu tivesse que escolher, o impacto social me atrairia um pouco mais do que o tecnológico.
Não porque as máquinas não sejam impressionantes — elas são — mas porque a Revolução Industrial foi, acima de tudo, uma revolução humana.
Por que o impacto social pesa mais?
1) Ela redesenhou a vida cotidiana
Antes, trabalho, família e comunidade estavam entrelaçados. Com as fábricas, o tempo passou a ser medido pelo relógio, não pelo sol. Jornadas longas, trabalho infantil e migração em massa para cidades mudaram para sempre o jeito de viver.
2) Criou conflitos que ainda ecoam hoje
A desigualdade entre donos de máquinas e trabalhadores deu origem a sindicatos, direitos trabalhistas, leis sociais e à própria noção de justiça no trabalho. Muitas discussões atuais — salário digno, carga horária, automação — nascem ali.
3) Forçou a sociedade a reagir ao progresso
Foi nesse período que a humanidade começou a perceber que inovação sem ética cobra um preço. Poluição, exploração e exaustão mostraram que tecnologia precisa de limites, algo extremamente atual na era da IA.
E o impacto tecnológico?
Ele foi o gatilho — vapor, ferrovias, telégrafo, produção em massa. Mas a tecnologia, sozinha, não explica a transformação. O que realmente mudou o mundo foi a reação humana a essas máquinas: organização, resistência, adaptação.
Conexão com o presente
A Revolução Industrial é o espelho da nossa era digital.
Hoje, a IA faz com o trabalho intelectual o que as máquinas fizeram com o trabalho físico.
A pergunta continua a mesma, dois séculos depois:
👉 Vamos deixar a tecnologia nos moldar — ou vamos moldá-la com consciência social?
Se aprendermos com o impacto social da Revolução Industrial, talvez consigamos viver a Revolução Digital com menos dor e mais sabedoria.
Vejo o impacto da tecnologia na vida cotidiana como ambivalente e profundamente humano — ela amplia quem somos, mas também expõe o que ainda não aprendemos a administrar.
O lado que expande a vida
A tecnologia encurtou distâncias, multiplicou vozes e democratizou o acesso. Hoje, aprender algo novo, trabalhar remotamente, criar um negócio ou manter laços afetivos à distância é parte do cotidiano. Isso é libertador.
Ela devolveu tempo, abriu possibilidades e colocou ferramentas poderosas nas mãos de indivíduos comuns — algo impensável há poucas décadas.
O lado que exige maturidade
Ao mesmo tempo, a tecnologia não é neutra. Ela molda hábitos, atenção, desejos e até emoções. Quando mal usada, gera dispersão, dependência, vigilância excessiva e relações superficiais.
O problema não é a tecnologia em si — é a ausência de consciência, limites e propósito no seu uso.
Onde a IA muda tudo
A inteligência artificial marca um ponto de virada. Pela primeira vez, nossas ferramentas não apenas executam, mas interpretam, sugerem e aprendem conosco.
Isso aumenta produtividade, criatividade e precisão — mas também nos obriga a responder perguntas inéditas:
- O que delegamos às máquinas?
- O que deve permanecer humano?
- Quem decide os critérios?
Minha visão em uma frase
Tecnologia é um amplificador moral: ela amplia tanto nossa sabedoria quanto nossas distrações.O futuro não depende de termos máquinas mais inteligentes, mas de sermos humanos mais lúcidos.
Se usarmos a tecnologia com intenção, ética e senso de limite, ela não nos substitui — nos potencializa.
Caso contrário, ela apenas acelera nossos desequilíbrios.
A revolução não é digital. É cultural, ética e interior.
Eu imagino a IA transformando os fundamentos do nosso futuro não como um substituto da vida humana, mas como uma força que revela o que realmente importa em ser humano.
1. Vida cotidiana: do esforço à intenção
A IA vai absorver silenciosamente grande parte do atrito do dia a dia — planejamento, organização, otimização, previsões. À medida que decisões rotineiras desaparecem, a vida passa a girar mais em torno da intenção do que da execução.
A pergunta central deixa de ser “Como faço isso?” e passa a ser “Por que isso merece o meu tempo?”
Se escolhermos bem, a IA nos devolve o recurso mais raro de todos: atenção.
2. Trabalho e propósito: do labor ao significado
Muitas tarefas desaparecerão, mas o trabalho não — ele vai se transformar.
O que permanece são funções baseadas em:
- julgamento em vez de repetição
- empatia em vez de mera obediência
- criatividade em vez de eficiência isolada
A IA força as sociedades a enfrentarem uma pergunta desconfortável, porém necessária:
O valor humano é medido pela produtividade ou pela contribuição, pelo cuidado e pela imaginação?
Esse ajuste pode ser doloroso, mas também libertador.
3. Educação: da memorização à sabedoria
Quando o conhecimento se torna instantaneamente acessível, a educação precisa migrar do acúmulo de fatos para a formação de mentes.
A IA pode personalizar o aprendizado, mas só humanos conseguem ensinar:
- raciocínio ético
- curiosidade
- dúvida
- responsabilidade
A sala de aula do futuro não gira em torno de respostas, mas de aprender a fazer perguntas melhores.
4. Relações e identidade: o efeito espelho
A IA nos devolve um reflexo de nós mesmos.
Ela absorve nossa linguagem, padrões, vieses e valores — obrigando a humanidade a confrontar:
- o que normalizamos
- o que recompensamos
- o que automatizamos sem refletir
Nesse sentido, a IA se torna um espelho moral.
Quando algo parece desumano, muitas vezes é porque foi treinado com práticas desumanas que já tolerávamos.
5. Ética e poder: o verdadeiro campo de disputa
O impacto mais profundo da IA não será técnico, mas político e ético.
Quem controla os dados?
Quem define prioridades?
Quem se beneficia da eficiência — e quem paga o preço?
O futuro depende de a IA ser tratada como:
- um bem público
- uma arma corporativa
- ou uma responsabilidade compartilhada
Não existe caminho neutro.
6. Visão de longo prazo: um novo renascimento ou uma erosão silenciosa
Cada grande salto tecnológico obrigou a humanidade a se redefinir.
A IA faz o mesmo — só que mais rápido.
Se guiada pela consciência, pode ajudar a construir:
- sistemas mais justos
- acesso inclusivo ao conhecimento
- saúde preventiva
- cidades sustentáveis
Se guiada apenas por lucro ou controle, corre o risco de:
- aprofundar desigualdades
- enfraquecer a autonomia
- corroer a confiança social
Em uma frase
A IA não decidirá nosso futuro — nossos valores decidirão.
A Inteligência Artificial é poderosa, mas não possui propósito próprio.
O futuro continua sendo um projeto humano.
Se esta era será um novo renascimento ou uma perda silenciosa de autonomia depende de uma única escolha:
unir inteligência à sabedoria, e velocidade ao cuidado.
